
- #Ipv4 address subnetting chart how to
- #Ipv4 address subnetting chart full
- #Ipv4 address subnetting chart zip
#Ipv4 address subnetting chart full
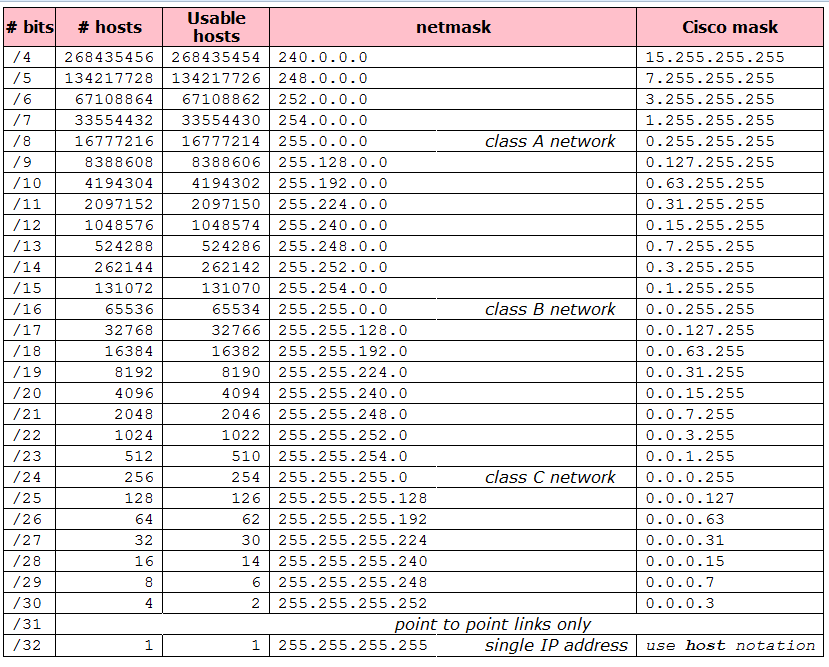
Here's what the full subnet mask table looks like. You can even steal bits from the host portion for the network. Subnetting enables you to choose the number of bits to use for the Network portion. These are the most common masks because they're the simplest, but when you need more than one network, you have to subnet.

If it were an /8 network, then only the first octet would be the network portion. If it were /16, then the first two octets would be the network portion, and the host portion would occupy the last two octets.

In this case, you could assign up to 254 hosts. The last octet is the host portion of the IP address. Notice that every host device in the network has the same first three octets. In this case, we're using 24 bits (or three octets) for the network. Note that the 255.0.0.0 mask can also be represented as a '/8' because it reserves 8 bits of the overall 32 bits used to describe an IPv4 address as the network portion.įor example, you might have a network with devices (known as hosts) with the following IP addresses: The black digits will be used for device IP addresses. In the following table, the red digits represent the bits used for the network. Subnet masks can also be defined in a more common 'slash' representation, known as CIDR notation. The host portion is like the house and street number.Ī subnet defines the number of bits, out of 32, used for the "network portion" of the address.
#Ipv4 address subnetting chart zip
The network portion is like the city, state, and zip code. There are two parts to an IP address: The network portion and the host portion. The process of taking an extensive network and splitting into smaller networks is known as subnetting - and it's freeing up more public IPv4 addresses. Luckily, the designers of IP addressing came up with a way to end this wasteful practice: Dividing networks using subnetting.
#Ipv4 address subnetting chart how to
How to define the network portion of a subnet IP addressĭuring the early stages of the internet, organizations assigned IP addresses like crazy until we nearly ran out. These are the most common octets you'll encounter in subnetting: When all the positions are "turned on," they add up to 255. So, 1 in the first and last positions "turn on" 128 and 1.Īdd up all the positions to get the decimal number: 128 + 1 = 129 Let's use this binary number, for example: 10000001Įvery 1 in a binary number "turns on" the number in its position. Hence the term octet or the 8-bit number grouping. Note that there are eight numbers between the decimal points.

The biggest IP address possible is 255.255.255.255 Why do octets only go up to 255? Because they're binary. These octets range in number from zero to 255. To make addresses more straightforward, they are divided into four 8-bit numbers - or octets - separated by a decimal point. Here's what an IP address looks like: 192.168.1.20Īn IPv4 address is a 32-bit number. To understand subnetting, you should first understand the decimal and binary structure of an IP address. A quick rundown of IP addresses and binary It's used to free up more public IPv4 addresses and segment networks for security and easier management. The quick definition: Subnetting is the process of taking a network and splitting it into smaller networks, known as subnets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
